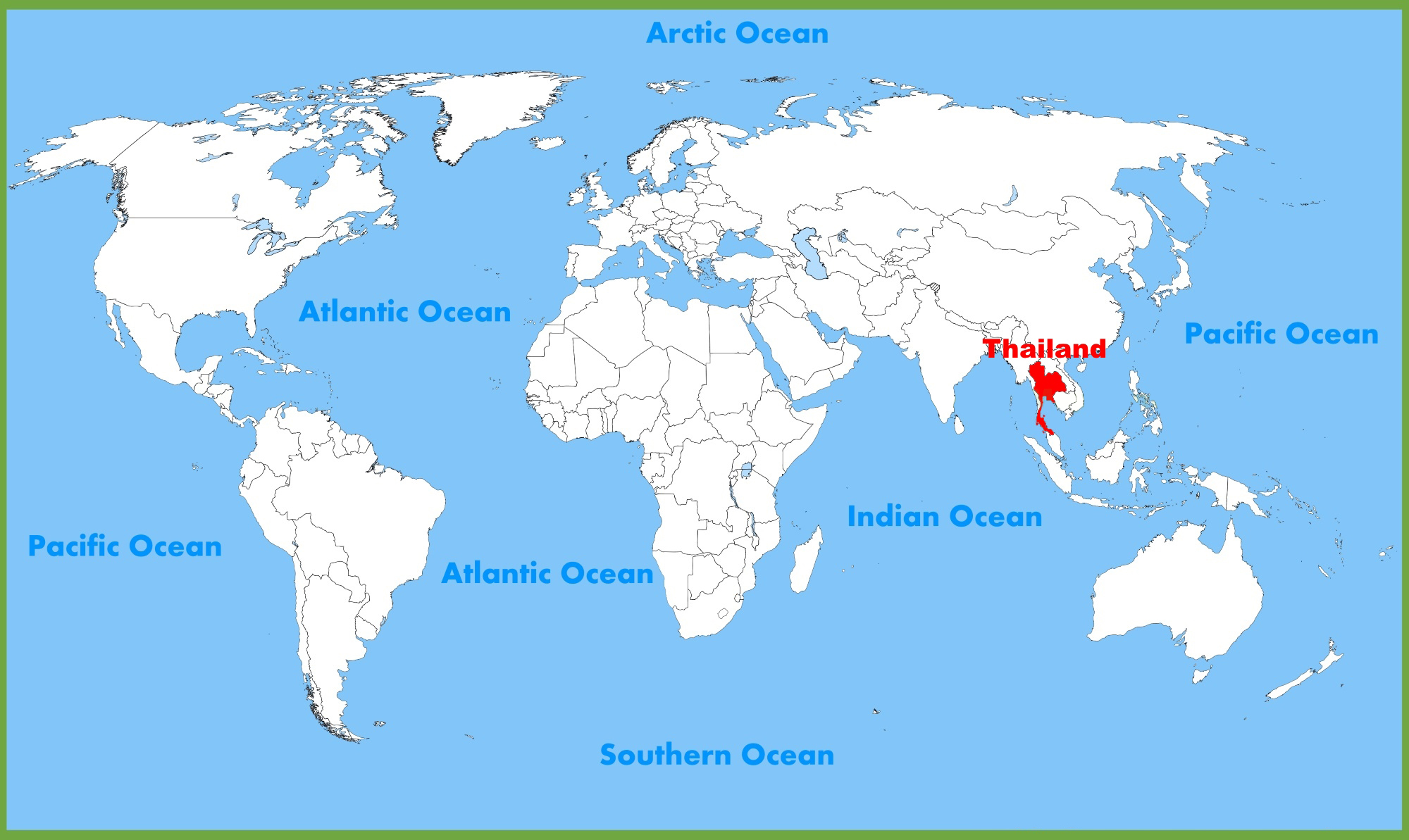
Key facts about Thailand
Official name: Kingdom of Thailand
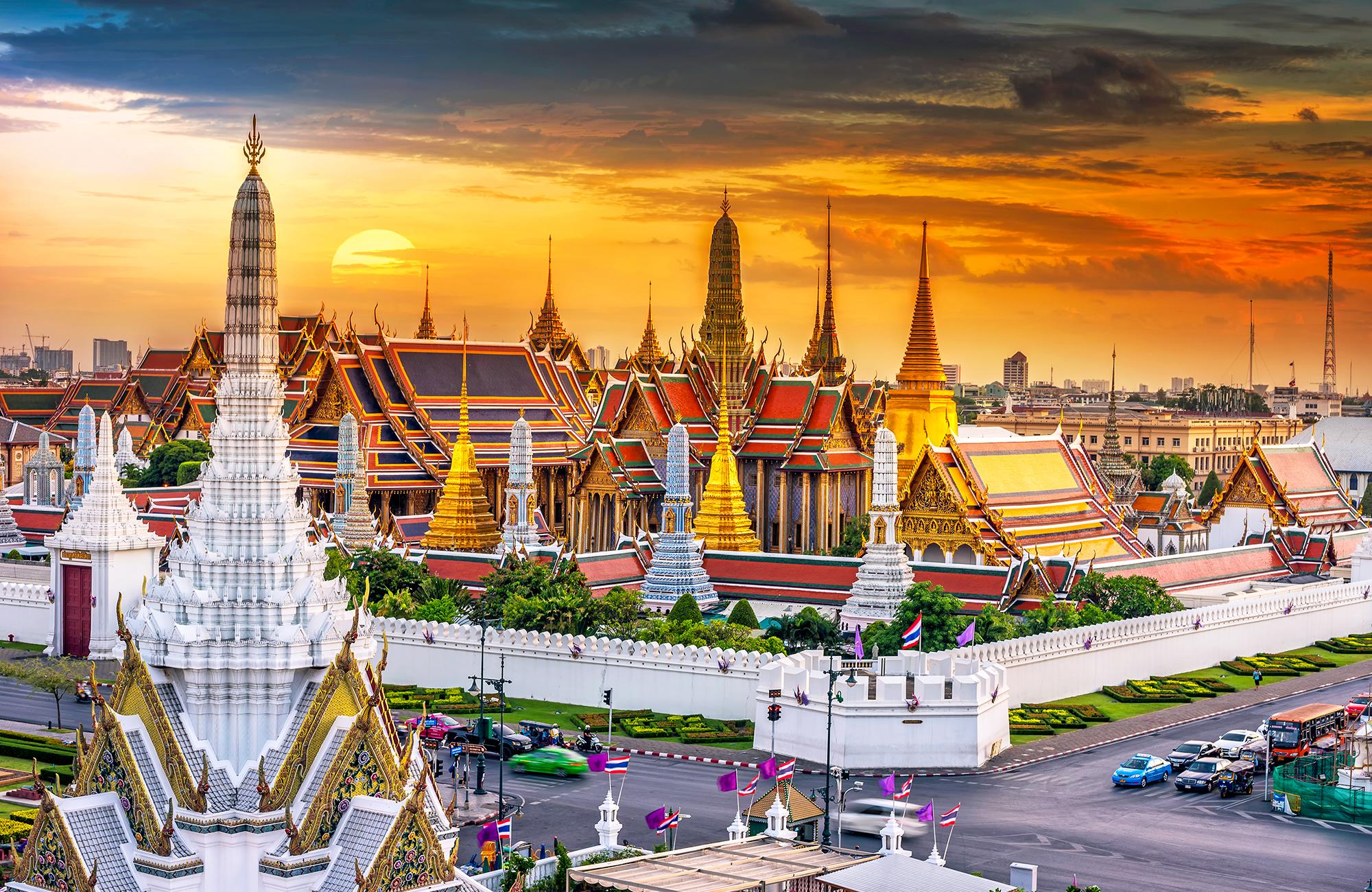
Capital: Bangkok
Geography: 76 provinces and two special local territories–Bangkok and Pattaya
Land area (2019): 513,120 sq km
Population (2019): 66.6 million
Head of government: Prime Minister General Prayut Chan-o-cha
National language: Thai
Currency: Thai Baht (THB)
Gross domestic product (GDP) (2019): 16,879 billion baht
GDP per capita (2019): 228,373 baht
Introduction
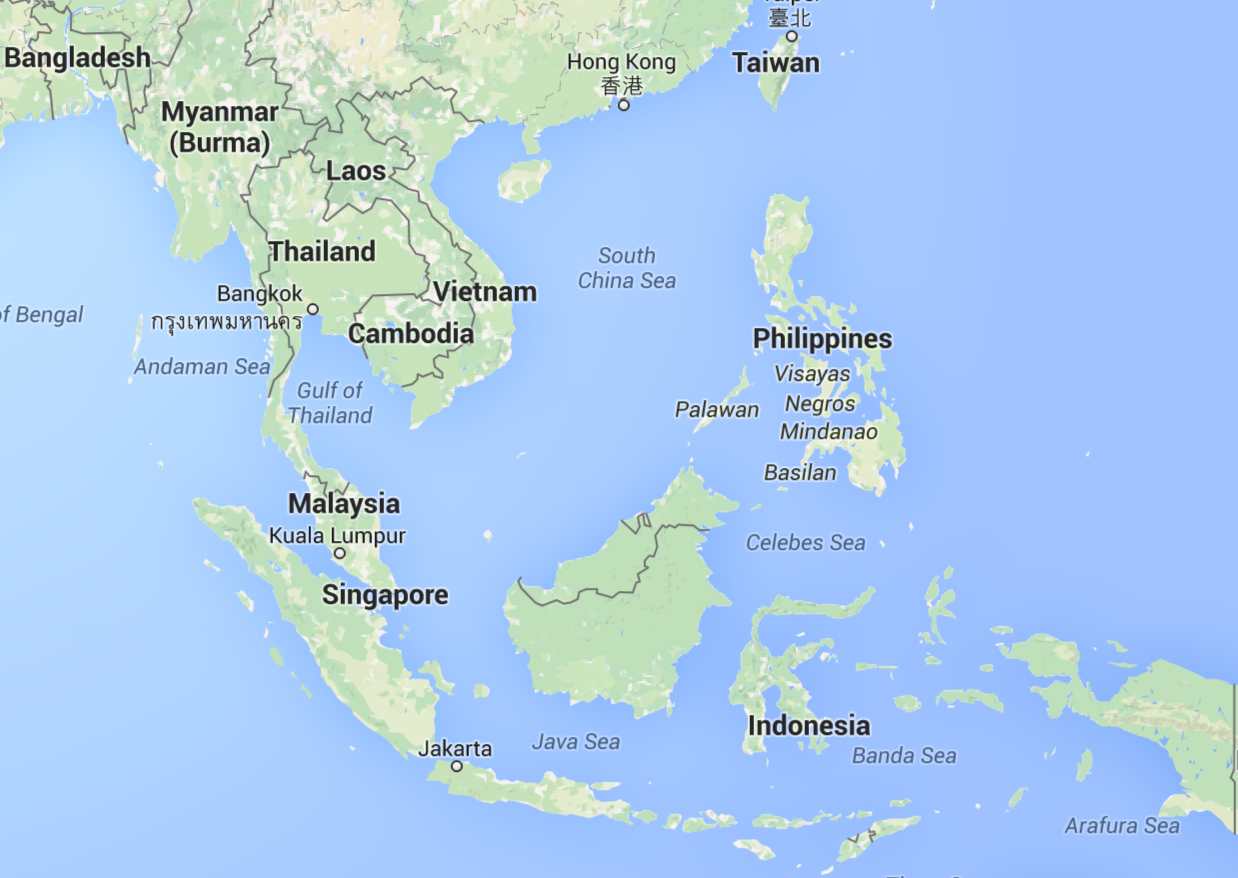
Thailand is situated in the heart of Southeast Asia, bordered by the Laos and Cambodia in the east; the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia in the south; the Andaman Sea and Myanmar in the west; and Laos and Myanmar in the north. It is spread over 513,120 sq km.
Demographic profile
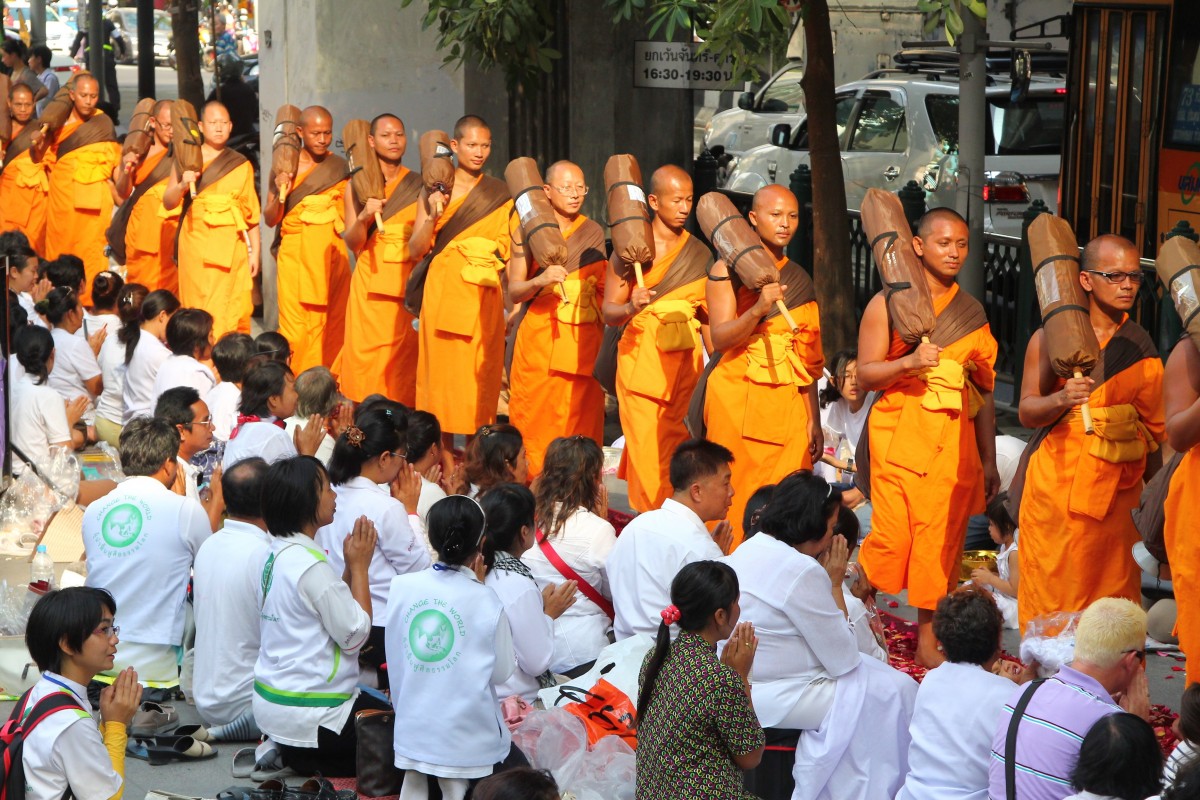
The total population of Thailand was almost 66.6 million in 2019. Around 48.96 percent (32.61 million persons) were male and 50.98 percent (33.95 million persons) female. Most of the population live in the northeastern region (33.05 percent), followed by the northern region (18.2 percent) and Bangkok (16.42 percent). Majority of the population are Buddhists, followed by Muslims and Christians.
Economy
Thailand has a mixed economy with the major economic sectors being agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, service and natural resource. Its GDP in 2019 was 16,879 billion baht.13 Its economic growth sectors include tourism, automotive and food manufacturing, which are supported by its well-developed transportation system, infrastructure and communications systems.
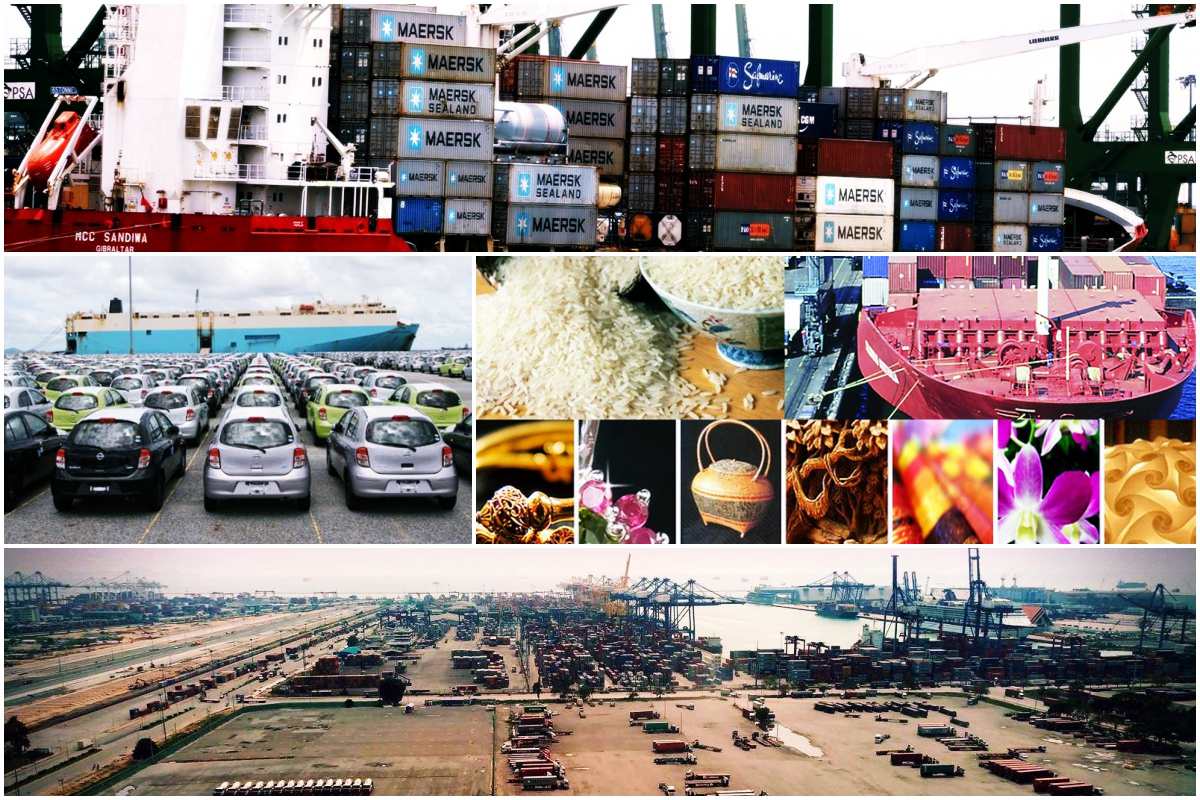
A leading exporter of rubber, Thailand also exports crops such as rice, vegetables and fruits. It is also famous for its livestock exports, as well as exports of freshwater fish and marine fishery. Its industrial exports include agro-industry, textile, electric appliance and automobiles. Important natural resources like limestone, gypsum, glass, sand, marble, tin and natural gas also contribute to the economy.
Industries
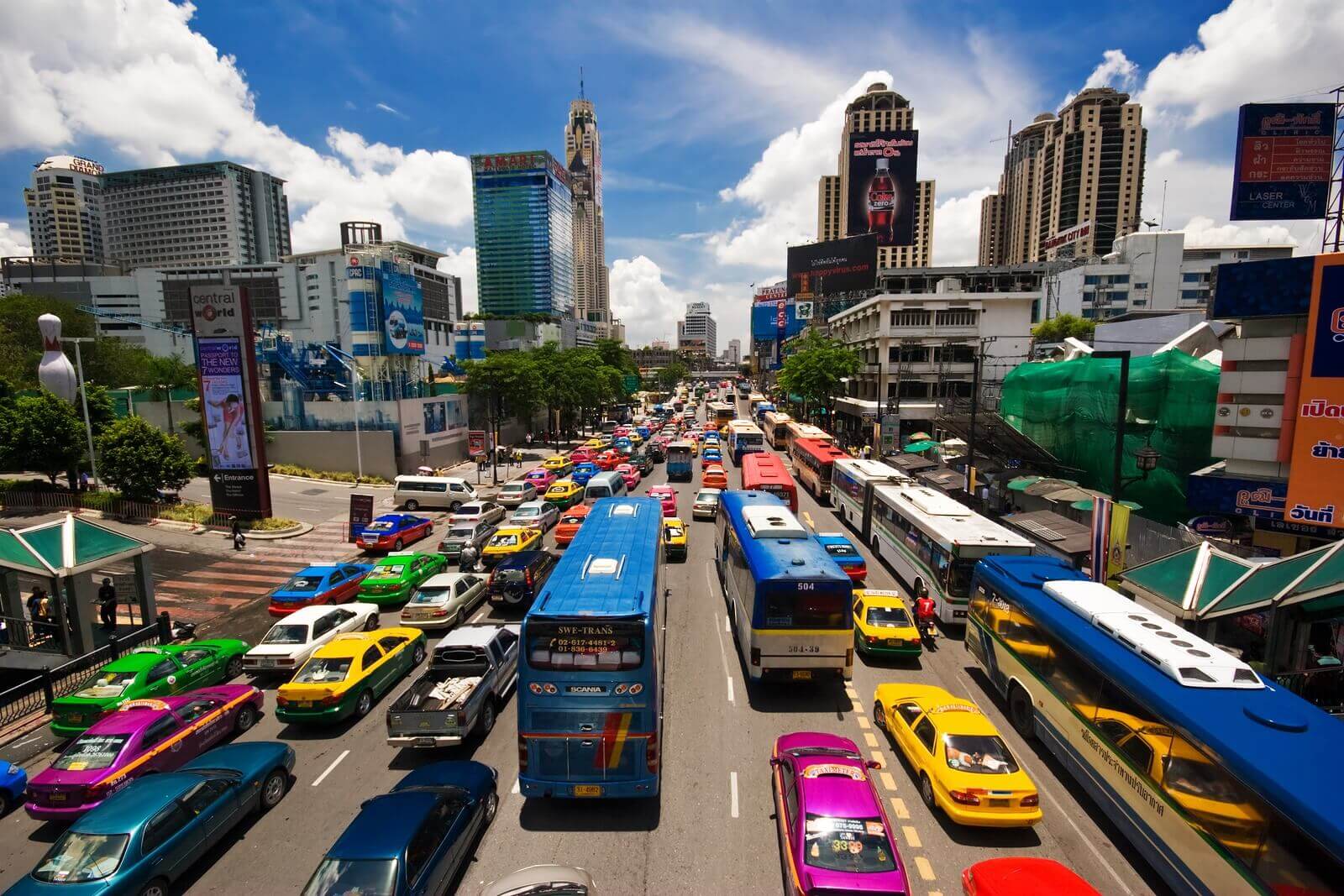
Thailand’s key business sectors include infrastructure development and manufacturing. The government approved a 3.3 trillion baht (US$101 billion) Infrastructure Development Plan (2015–2022) that aims to improve Thailand’s transport links (railways, roads, water transportation, aviation and mass transit projects), both within Thailand and with its neighbours.
Thailand has the fourth largest consumer market in ASEAN. Its unemployment rate is at a low one percent and the country has a purchasing power of an estimated US$6,000. In recent years, the purchasing power outside of capital city Bangkok has also grown.
The Thai automotive sector is the largest in ASEAN. However, the industry has been impacted by the global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) in recent years. Hence, the ‘Thai government is persistently trying to encourage the manufacturing of EVs and high-tech auto parts through promotion of incentive packages.’
Tourism
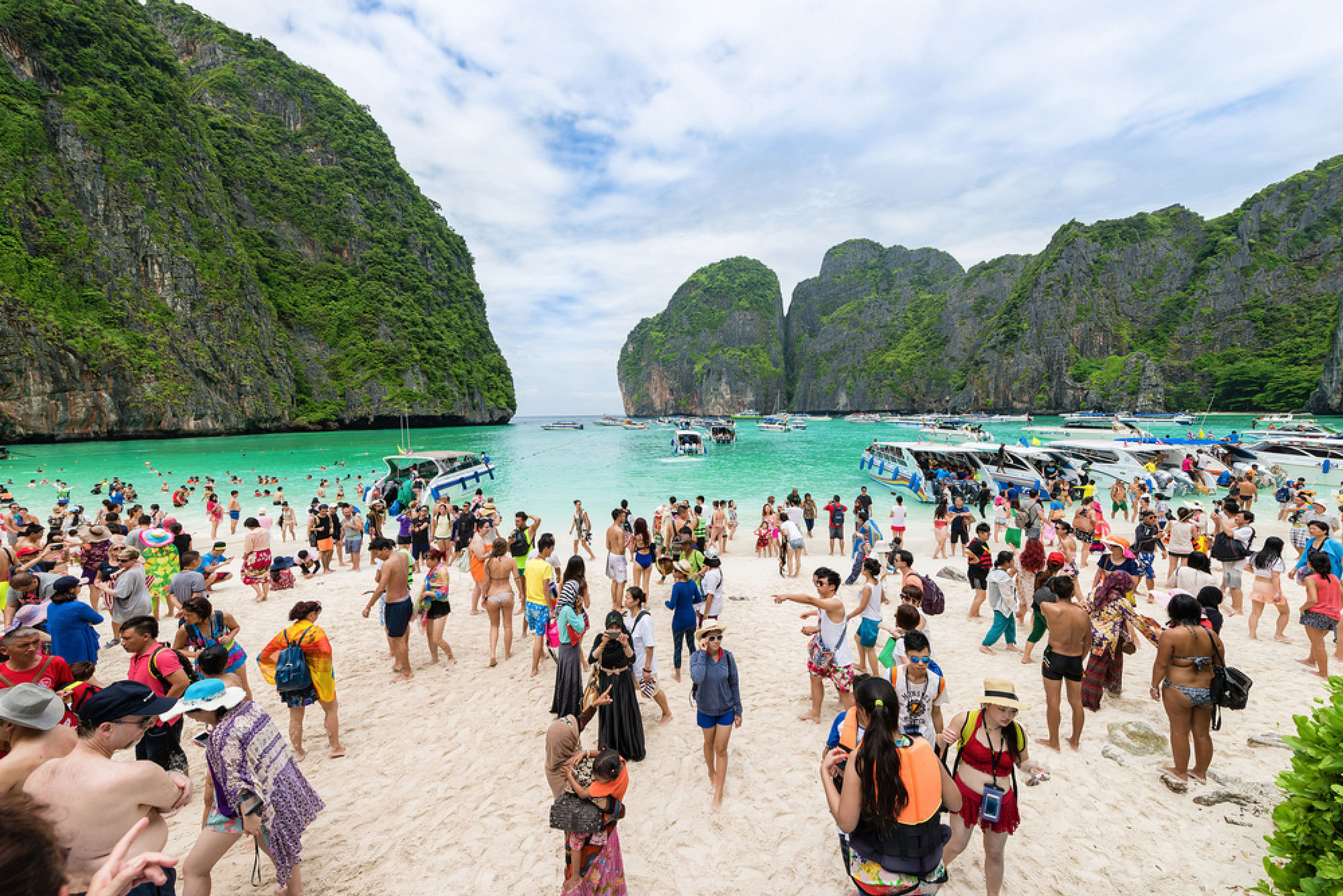
Thailand is home to Buddhist temples, exotic wildlife and spectacular islands. It is also known for its fascinating history, unique culture and delectable local food. The tourism industry plays an important role in the Thai economy and contributes an estimated 18.4 percent to the national GDP. The tourism sector not only depends on foreign visitors but also domestic tourists whose number dwarfs that of foreign tourists. In 2019, Thailand had 39,797,406 visitors.
Thailand 4.0
Thailand 4.0 is an economic model that aims to ‘unlock Thailand from several economic challenges and help the country break free from the middle-income trap’. It comprises four objectives: economic prosperity–to create a value-based economy that is driven by innovation, technology and creativity; social well-being–to create a society that moves forward without leaving anyone behind (inclusive society) through realisation of the full potential of all members of society; raising human values–to transform cost-effective labour into a skilled workforce; and environmental protection–to become a liveable society that possesses an economic system capable of adjusting to climate change and low carbon society.






 中文
中文 English
English Back
Back Business ID:16319330
Business ID:16319330 Tulika 31-217, Tallinn, Estonia
Tulika 31-217, Tallinn, Estonia +372 5883 9464
+372 5883 9464 majianming7176@sina.com
majianming7176@sina.com www.pandahappy.net
www.pandahappy.net
